Formation of cluster crystals in an ultra-soft potential model on a spherical surface
Abstract
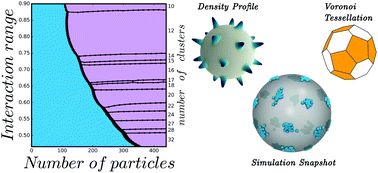
We investigate the formation of cluster crystals with multiply occupied lattice sites on a spherical surface in systems of ultra-soft particles interacting via repulsive, bounded pair potentials. Not all interactions of this kind lead to clustering: we generalize the criterion devised in C. N. Likos et al., Phys. Rev. E, 2001, 63, 031206 to spherical systems in order to distinguish between cluster-forming systems and fluids which display reentrant melting. We use both DFT and Monte Carlo simulations to characterize the behavior of the system, and obtain semi-quantitative agreement between the two. We find that the number of clusters is determined by the ratio between the size σ of the ultra-soft particles and the radius R of the sphere in such a way that each stable configuration spans a certain interval of σ/R. Furthermore, we study the effect of topological frustration on the system due to the sphere curvature by comparing the properties of disclinations, i.e., clusters with fewer than six neighbors, and non-defective clusters. Disclinations are shown to be less stable, contain fewer particles, and be closer to their neighbors than other lattice points: these properties are explained on the basis of geometric and energetic considerations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...