Dissipative assemblies that inhibit their deactivation†
Abstract
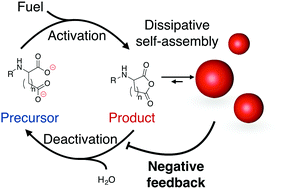
Dissipative self-assembly is a process in which energy-consuming chemical reaction networks drive the assembly of molecules. Prominent examples from biology include the GTP-fueled microtubule and ATP-driven actin assembly. Pattern formation and oscillatory behavior are some of the unique properties of the emerging assemblies. While artificial counterparts exist, researchers have not observed such complex responses. One reason for the missing complexity is the lack of feedback mechanisms of the assemblies on their chemical reaction network. In this work, we describe the dissipative self-assembly of colloids that protect the hydrolysis of their building blocks. The mechanism of inhibition is generalized and explored for other building blocks. We show that we can tune the level of inhibition by the assemblies. Finally, we show that the robustness of the assemblies towards starvation is affected by the degree of inhibition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...