Design and preparation of sandwich-like polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sponges with super-low ice adhesion
Abstract
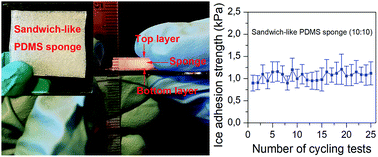
The mitigation of ice on exposed surfaces is of great importance to many aspects of life. Ice accretion, however, is unavoidable as time elapses and temperature lowers sufficiently. One practical solution is to reduce the ice adhesion strength on a surface to as low as possible, by either decreasing the substrate elastic modulus, lowering surface energy or increasing the length of cracks at the ice–solid interface. Herein, we present a facile preparation of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based sandwich-like sponges with super-low ice adhesion. The weight ratio of the PDMS prepolymer to the curing agent is tuned to a lower surface energy and elastic modulus. The introduction of PDMS sponge structures combined the advantages of both a reduced apparent elastic modulus and most importantly, the macroscopic crack initiators at the ice–solid interface, resulting in dramatic reduction of the ice adhesion strength. Our design of sandwich-like sponges achieved a low ice adhesion strength as low as 0.9 kPa for pure PDMS materials without any additives. The super-low ice adhesion strength remains constant after 25 icing and deicing cycles. We thus provide a new and low-cost approach to realize durable super-low ice adhesion surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...