Nanoparticle packing within block copolymer micelles prepared by the interfacial instability method†
Abstract
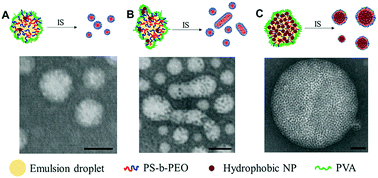
The interfacial instability method has emerged as a viable approach for encapsulating high concentrations of nanoparticles (NPs) within morphologically diverse micelles. In this method, transient interfacial instabilities at the surface of an emulsion droplet guide self-assembly of block co-polymers and NP encapsulants. Although used by many groups, there are no systematic investigations exploring the relationship between NP properties and micelle morphology. Here, the effect of quantum dot (QD) and superparamagnetic iron oxide NP (SPION) concentration on the shape, size, and surface deformation of initially spherical poly(styrene-b-ethylene oxide) (PS-b-PEO) micelles was examined. Multi-NP encapsulation and uniform dispersion within micelles was obtained even at low NP concentrations. Increasing NP concentration initially resulted in larger numbers of elongated micelles and cylinders with tightly-controlled diameters smaller than those of spherical micelles. Beyond a critical NP concentration, micelle formation was suppressed; the dominant morphology became densely-loaded NP structures that were coated with polymer and exhibited increased polydispersity. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) revealed that NPs in densely-loaded structures can be well-ordered, with packing volume fractions of up to 24%. These effects were enhanced in magnetic composites, possibly by dipole interactions. Mechanisms governing phase transitions triggered by NP loading in the interfacial instability process were proposed. The current study helps establish and elucidate the active role played by NPs in directing block copolymer assembly in the interfacial instability process, and provides important guiding principles for the use of this approach in generating NP-loaded block copolymer composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
