Formation of complexes in aqueous solutions of amphiphilic triblock polyelectrolytes of different topologies and an oppositely charged protein†
Abstract
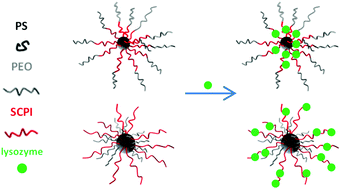
The complexation of lysozyme with aggregates from two triblock amphiphilic polyelectrolytes of the same blocks but different topologies and block molar masses, namely PS-b-SCPI-b-PEO and SCPI-b-PS-b-PEO, is investigated by scattering and spectroscopy methods. Light scattering reveals that the interaction with lysozyme causes shrinkage of the self-assembled nanoparticles in the case of the hydrophobic–polyelectrolyte–hydrophilic sequence. In the polyelectrolyte–hydrophobic–hydrophilic sequence, the opposite trend is observed. Small angle neutron scattering confirms the existence of micellar and fractal aggregates and the complexation with lysozyme. The pH-dependence of the interactions and the stability of the hybrid protein/polymer nanoparticles upon salt addition are tested. The native conformation of the protein is found to be preserved during complexation. This study reveals that both micellar and fractal aggregates made of amphiphilic triblock polyelectrolytes are capable of loading with oppositely charged proteins in a controllable manner, tuned primarily by the structure of the triblock terpolymer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...