Mechanism of the formation of microphase separated water clusters in a water-mediated physical network of perfluoropolyether tetraol†
Abstract
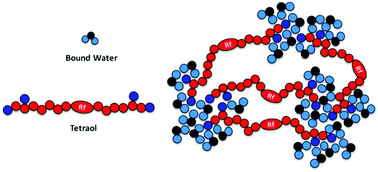
Perfluoropolyether tetraol (PFPE tetraol) possesses a hydrophobic perfluoropolyether chain in the backbone and two hydroxyl groups at each chain terminal, which facilitates the formation of hydrogen bonds with water molecules resulting in the formation an extended physical network. About 3 wt% water was required for the formation of the microphase separated physical network of PFPE tetraol. The mechanism responsible for the microphase separation of water clusters in the physical network was studied using a combination of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and DSC. MD simulation studies provided evidence for the formation of clusters in the PFPE tetraol physical network and the size of these clusters increased gradually with an increase in the extent of hydration. Both MD simulations and NMR spectroscopy studies revealed that these clusters position themselves away from the hydrophobic backbone or vice versa. The presence of intra- and inter-chain aggregation possibility among hydrophilic groups was evident. DSC results demonstrated the presence of tightly and loosely bound water molecules to the terminal hydroxyl groups of PFPE tetraol through hydrogen bonding. The data from all the three techniques established the formation of a physical network driven by hydrogen bonding between the hydrophilic end groups of PFPE tetraol and water molecules. The flexible nature of the PFPE tetraol backbone and its low solubility parameter favour clustering of water molecules at the terminal groups and result in the formation of a gel.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...