Core–shell structural PANI-derived carbon@Co–Ni LDH electrode for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors†
Abstract
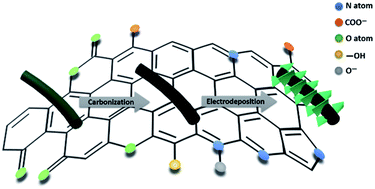
Carbon/metal nanocomposites have been considered promising electrode materials for application in supercapacitors owing to their combination of good electrical conductivity, excellent cycle stabilities of the electronic double layer capacitor (EDLC) and high specific capacitance of the pseudocapacitor. Here, a core–shell structured polyaniline derived carbon nanowire@Co–Ni layered double hydroxide (PANC@Co–Ni LDH) nanomaterial was successfully synthesized via a novel facile electrodeposition–carbonization–electrodeposition route. The core-like PANC full of N atoms retains its innate long-chain structure and provides a lot of active sites for the uniform growth of the shell-like Co–Ni LDH, resulting in a cross-linked active network structure with numerous electroactive sites, abundant pores, and adequate large space and reaction interface, which contribute to the rapid diffusion and transportation of the electrolyte ions and electrons. Therefore, as-obtained PANC@Co–Ni LDH showed a high specific capacitance of 1529.52 F g−1 at 0.5 A g−1 in a three electrode system and offered outstanding rate properties with no obvious capacitance attenuation (1425.17 F g−1) when the current density increased to 10 A g−1. Moreover, an asymmetric supercapacitor using PANC@Co–Ni LDH as the positive electrode and PANC as the negative electrode was fabricated, which revealed a high specific capacitance of 214.28 F g−1 and superior energy density of 38.73 W h kg−1 with a power density of 0.92 kW kg−1, suggesting great potential in practical energy storage devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...