Sequential hydrogen production system from formic acid and H2/CO2 separation under high-pressure conditions†
Abstract
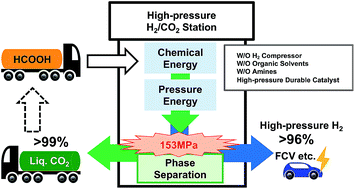
Hydrogen (H2) production from formic acid (FA) is highly attractive as a sustainable energy source from the interconversion between CO2 and FA. Dehydrogenation of FA at high pressures has advantages over a reaction at atmospheric conditions for the separation of H2 and CO2 due to the reaction and the volumetric energy density of H2. We demonstrated the continuous production of high-pressure H2 by catalytic decomposition of FA, and subsequent separation of H2 and CO2 from FA decomposition gas (H2 : CO2 = 1 : 1) using the phase change phenomenon at low temperatures while maintaining high pressure. An iridium aqua complex coordinated with a bidentate pyridyl-imidazoline ligand catalyzed the dehydrogenation of FA with high efficiency at a pressure as high as 153 MPa. The Ir catalyst was found to be stable under continuous addition of neat FA at high pressures. The generation time and rate of high-pressure H2 were controlled by feeding neat FA to the aqueous reaction system. Using our combined system, more than 99 mol% of H2 (96 mol% of purity) and 94 mol% of CO2 (99 mol% of purity) were separately obtained from FA as a gas and liquid, respectively, under the high-pressure conditions without any mechanical compression.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
