Higher efficiency perovskite solar cells using Au@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles
Abstract
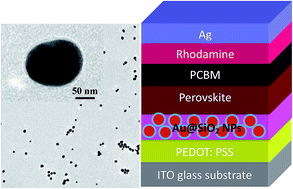
In this work, we improved photovoltaic performance by about 27% in planar p-i-n perovskite solar cells (PSCs) using plasmonic Au@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles (NPs). The devices have an architecture of ITO glass/PEDOT:PSS/perovskite(CH3NH3PbI3)/PCBM/Rhodamine/Ag. Four batches of devices were fabricated with different concentrations of Au@SiO2 NPs ranging from 0.4 to 1.6 wt% with an interval of 0.4 wt%. The Au@SiO2 NPs were integrated at the interface between the PEDOT:PSS layer and the active perovskite layer. At an optimized concentration of 1.2 wt% Au@SiO2 NPs, the PSCs achieved 25.1% of enhancement in photocurrent from 17.45 to 22.35 mA cm−2 and an improvement of 27.3% in power conversion efficiency (PCE) from 11.44 to 14.57%. This significant improvement in device performance is attributed to the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of Au@SiO2 NPs, which enhanced the light absorption in the active perovskite layer. The transient photocurrent and photovoltage measurements revealed that PSCs with Au@SiO2 NPs have a faster charge transport time and longer recombination lifetime than those without Au@SiO2 NPs. These results demonstrate that plasmonic metal nanoparticles substantially improved the efficiency of PSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
