Pt-grown carbon nanofibers for enzymatic glutamate biosensors and assessment of their biocompatibility†
Abstract
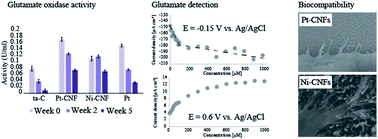
Application-specific carbon nanofibers grown from Pt-catalyst layers have been shown to be a promising material for biosensor development. Here we demonstrate immobilization of glutamate oxidase on them and their use for amperometric detection of glutamate at two different potentials. At −0.15 V vs. Ag/AgCl at concentrations higher than 100 μM the oxygen reduction reaction severely interferes with the enzymatic production of H2O2 and consequently affects the detection of glutamate. On the other hand, at 0.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl enzyme saturation starts to affect the measurement above a glutamate concentration of 100 μM. Moreover, we suggest here that glutamate itself might foul Pt surfaces to some degree, which should be taken into account when designing Pt-based sensors operating at high anodic potentials. Finally, the Pt-grown and Ni-grown carbon nanofibers were shown to be biocompatible. However, the cells on Pt-grown carbon nanofibers had different morphology and formation of filopodia compared to those on Ni-grown carbon nanofibers. The effect was expected to be caused rather by the different fiber dimensions between the samples than the catalyst metal itself. Further experiments are required to find the optimal dimensions of CNFs for biological purposes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...