Green synthesis of safe zero valent iron nanoparticles by Myrtus communis leaf extract as an effective agent for reducing excessive iron in iron-overloaded mice, a thalassemia model
Abstract
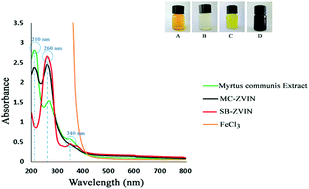
Green synthesis of Myrtus communis-Zero Valent Iron Nanoparticles (MC-ZVINs) was carried out in an alkaline environment. These nanoparticles were introduced for testing in vivo iron chelation in an iron-overload thalassemia model in mice. The MC-ZVINs were characterized by the use of imaging (electron microscopy) and spectroscopic (UV-vis and infrared absorption, dynamic light scattering and X-ray diffraction) methods. These methods demonstrated that some polyphenols are bound to the surfaces of the MC-ZVINs as a capping/stabilizing agent. The MC-ZVINs and defroxamine were injected 5 times a week over 4 weeks. The total iron and Fe3+ content of serum was determined by microwave plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy and an Fe3+ ion measuring kit respectively and liver enzyme levels were evaluated with an auto-analyzer. Morphological changes of the liver were examined by haematoxylin and eosin and Prussian blue staining. Additionally, the bioactivity of the iron nanoparticles was checked by DPPH and nitric oxide radical scavenging activity, reducing power and iron (Fe2+) chelating ability. Iron-overloaded mice treated with the MC-ZVINs, indicated a drastic reduction in serum iron content when compared with the control groups and those treated with defroxamine. MC-ZVINs exhibit satisfactory potency to chelate excessive iron in mice. The data collected in this study will be helpful for selecting the most appropriate operational conditions for synthesizing green ZVINs in biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...