Ternary composites by an in situ hydrolytic polymerization process†
Abstract
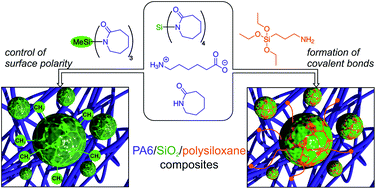
Polyamide 6/modified silica composite materials have been prepared by a coupled polymerization procedure. For this purpose, the three-component-system we presented in a previous publication, consisting of ε-aminocaproic acid (ε-ACA), ε-caprolactam (ε-CL), and 1,1′,1′′,1′′′-silanetetrayltetrakis-(azepan-2-one) (Si(ε-CL)4), has been combined with other silicon monomers with one or two methyl groups (MeSi(ε-CL)3 and Me2Si(ε-CL)2). The simultaneous polymerization of ε-CL and silicon monomers leads to the in situ formation of silica/polysiloxane particles and the surrounding polyamide 6 matrix in one step. Moreover, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane has been added to the three-component-system to achieve covalent bonding between organic and inorganic phases and to inhibit agglomeration of the silica particles. Chemical structures and morphologies of the composites have been investigated by solid-state NMR and FTIR spectroscopy as well as electron microscopy and SEC measurements. Structural effects on thermal properties have been studied by DSC and TGA measurements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...