The feasibility of enhanced biological phosphorus removal in the novel oxic/extended idle process using fermentation liquid from sludge fermentation
Abstract
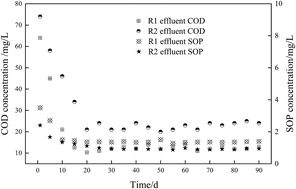
Carbon sources are essential for biological phosphorus removal (BPR); the carbon sources, however, are often inadequate in municipal wastewater treatment plants. This study demonstrated the feasibility of sludge fermentation liquid enhanced by biosurfactant alkylpolyglycosides (APG) as carbon sources to improve the performance of BPR in the novel oxic/extended idle (O/EI) reactor and the underlying mechanism was also investigated. The results showed that APG induced fermentation liquid could enhance the BPR performance in the O/EI reactor, and the BPR efficiency was 95.2%, which was significantly higher than that in the conventional anaerobic/oxic (A/O) reactor. Mechanism investigation showed that compared with the A/O reactor, the O/EI reactor enriched more polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) (38.2%), but less glycogen accumulating organisms (GAOs) when the APG-induced fermentation liquid was used as carbon source. The transformations of the polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and glycogen in the O/EI reactor were lower than those in the A/O reactor. Further study found that the activities of polyphosphate kinase (PPK) and acetyl-CoA synthases (ACS) in the O/EI reactor were significantly higher than those of the A/O reactor, which was consistent with the higher BPR efficiency in the O/EI reactor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...