Novel chiral aggregation induced emission molecules: self-assembly, circularly polarized luminescence and copper(ii) ion detection†
Abstract
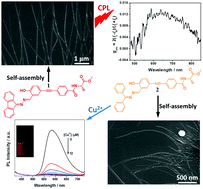
This work provides a feasible strategy for future design of CPL materials and ion sensors. By introducing chiral alanine to hydrazone derivatives, two novel chiral molecules 1 and 2 with aggregation-induced emission enhanced (AIEE) characteristics were designed and synthesized. Molecule 1 had the two phenyl groups connecting to hydrazone covalently bonded, so its fluorophore is more conjugated than that of 2. This subtle structural variation between 1 and 2 had a considerable influence on their photophysical properties, chiral optical properties and self-assembly behaviors. Both kinds of molecules could self-assemble into long helical nanofibers with lengths up to several microns upon aggregation. They both possessed AIEE properties, but 1 emitted red fluorescence and 2 had yellow fluorescence upon aggregation. They also had aggregation induced circular dichroism (CD) and circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) properties, but 1 had better performance because its fluorophore was more conjugated than that of 2. However, only 2 had a specific interaction with Cu2+ and it showed a highly selective and sensitive “turn-off” fluorescence response to Cu2+.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Progress on Aggregation-Induced Emission


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...