Ba2ZnSc(BO3)3 and Ba4Zn5Sc2(BO3)8: first examples of borates in the Zn–Sc–B–O system featuring special structure configurations†
Abstract
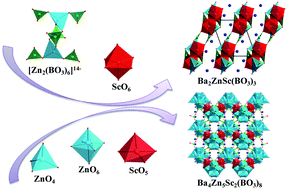
As the first reported examples of borates in the Zn–Sc–B–O system, Ba2ZnSc(BO3)3 and Ba4Zn5Sc2(BO3)8 were synthesized through a high-temperature solution method. The structure of Ba2ZnSc(BO3)3 can be described as ZnO4 tetrahedra connecting ScO6 octahedra to form a [ZnScO9]13− dimer, which further bonds with seven BO3 triangles to form a 2∞[ZnSc(BO3)3] layer, and the Ba atoms distribute in the voids between the layers. In contrast, in Ba4Zn5Sc2(BO3)8, Zn–O chains composed of 4- and 6-coordinated Zn atoms link with Sc2O8 dimers to form a Zn–Sc–O layer, and the BO3 triangles and Ba atoms fill in the voids between the layers. Interestingly, the special [Zn2(BO3)6]14− cluster is found in Ba2ZnSc(BO3)3, which is different from the 2D layers or 3D frameworks of the Zn–B–O configurations in other zincoborates. Moreover, the lowest-coordinated ScO5 polyhedra, as well as the coexistence of two types of ZnOn units (n = 4 and 6), are observed for the first time in Ba4Zn5Sc2(BO3)8. These fascinating results can promote the design of novel borates with BO3 units and enrich the borate structure chemistry.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles for 2018


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...