Polymerization of 1-chloro-2-phenylacetylene by cationic monoanionic tridentate (S,S)-bis(oxazolinylphenyl)amido-ligated palladium catalysts: is it a coordination–insertion mechanism?†
Abstract
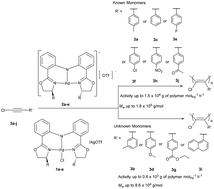
A series of air-stable monoanionic tridentate (S,S)-bis(oxazolinylphenyl)amido-ligated palladium (Pd) chloride complexes (R2-(S,S)-BOPA)PdCl (1a–e) (1a: R = Ph; 1b: R = iPr; 1c: R = Bn; 1d: R = Et; 1e: R = Me) have been synthesized and structurally characterized. The double decomposition reaction of these Pd chloride complexes 1a–e with one equivalent of silver trifluoromethanesulfonate (AgOTf) quantitatively affords the corresponding cationic monoanionic tridentate Pd species [(R2-(S,S)-BOPA)Pd]+[OTf]− (2a–e) as characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Such single-component or in situ generated cationic Pd species are active for the polymerization of once used 1-chloro-2-phenylacetylenes (CPAs) bearing nonpolar, halogen, and polar substituents (3a: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-Me; 3c: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-Me; 3c: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H5; 3e: Cl–C
C–C6H5; 3e: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-F; 3f: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-F; 3f: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-Cl; 3h: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-Cl; 3h: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-NO2; 3j: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-NO2; 3j: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-COCH3) even in air, affording partly soluble cis-selective poly(1-chloro-2-phenylacetylene)s (PCPAs) with high molecular weights and broad molecular weight distributions similar to those obtained by the known Pd catalysts. More significantly, the single-component cationic Pd species can also promote the polymerization of unused CPAs (3b: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-COCH3) even in air, affording partly soluble cis-selective poly(1-chloro-2-phenylacetylene)s (PCPAs) with high molecular weights and broad molecular weight distributions similar to those obtained by the known Pd catalysts. More significantly, the single-component cationic Pd species can also promote the polymerization of unused CPAs (3b: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–m-Me; 3d: Cl–C
C–C6H4–m-Me; 3d: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-OMe; 3g: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-OMe; 3g: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C6H4–p-COOEt; 3i: Cl–C
C–C6H4–p-COOEt; 3i: Cl–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–(1-C10H7)) for the first time, providing novel cis-selective PCPAs which are unavailable from traditional catalysts. Similar to the known Pd catalysts, a possible coordination–insertion mechanism is proposed by means of 1H NMR, IR, and ESI-MS spectroscopies, which provides a new insight into the initiation and termination polymerization process of CPAs catalyzed by these cationic monoanionic tridentate (S,S)-bis(oxazolinylphenyl)amido-ligated Pd catalysts.
C–(1-C10H7)) for the first time, providing novel cis-selective PCPAs which are unavailable from traditional catalysts. Similar to the known Pd catalysts, a possible coordination–insertion mechanism is proposed by means of 1H NMR, IR, and ESI-MS spectroscopies, which provides a new insight into the initiation and termination polymerization process of CPAs catalyzed by these cationic monoanionic tridentate (S,S)-bis(oxazolinylphenyl)amido-ligated Pd catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...