Diblock copolymer glyco-nanomicelles constructed by a maltoheptaose-based amphiphile for reduction- and pH-mediated intracellular drug delivery†
Abstract
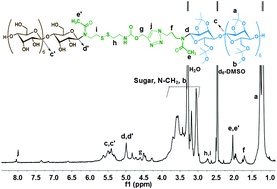
A new type of reduction- and pH-mediated glyco-polymeric micelles was synthesized for the antitumor drug doxorubicin (DOX) delivery in this study. The micelles were constructed by a diblock copolymer (MH-S-S-AcMH) with a disulfide linkage between hydrophilic block maltoheptaose (MH) and hydrophobic block acetalated maltoheptaose (AcMH). The experimental results showed that the amphiphilic MH-S-S-AcMH with 20 nm average size could self-assemble into micelles under physiological conditions and rapidly release the conjugated drug DOX when exposed to weakly acidic (pH = 5) and reductive (10 mM DTT) environment. Fluorescence microscopy detection indicated that drug carriers can be endocytosed effectively, making the anticancer agents flow into cells and suppress the growth of HeLa tumor cells. Compared with DOX at higher dosage and MH-S-S-AcMH micelles which are non-toxic to tumor cells, cytotoxicity assays manifested that the DOX-loaded MH-S-S-AcMH micelles exhibited better toxicity to HeLa tumor cells. According to these results, the copolymer mentioned above as practically non-toxic, highly stable, novel reduction- and pH-mediated glyco-polymeric micelles could be employed in improving drug delivery efficiency and enhancing anticancer efficacy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...