Irradiation with 310 nm and 340 nm ultraviolet light-emitting-diodes can improve atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice†
Abstract
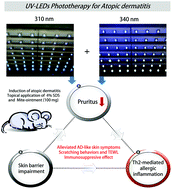
Ultraviolet (UV) light produces an immunomodulatory effect on the skin and is widely used for the treatment of chronic inflammatory skin diseases. UV light emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) are a new and promising source of UV radiation. However, their mechanism of action remains largely unknown. In this study, we tested the safety and effectiveness of UV-LED irradiation for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) in an NC/Nga mouse model. Mice were divided into seven groups of eight mice each. Application of Dermatophagoides farinae (Df) extract ointment for four weeks induced AD-like skin lesions. Subsequently, the mice were exposed to UV-LEDs, narrow band UVB, or UVA irradiation three times per week. We assessed the immunosuppressive effects of 310 nm (50 mJ cm−2) and 340 nm (5 J cm−2) UV-LED irradiation. Histological analyses using hematoxylin–eosin, toluidine blue, and immunohistochemical staining were performed. In addition, the serum levels of IgE, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). UV-LED irradiation significantly alleviated AD-like skin symptoms, including edema, erythema, dryness, and itching, by modulating Th1 and Th2 responses, transepidermal water loss (TEWL), and scratching behavior in NC/Nga mice. These results suggest that UV-LEDs can improve the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...