Cyclic arylopeptoid oligomers: synthesis and conformational propensities of peptide-mimetic aromatic macrocycles†
Abstract
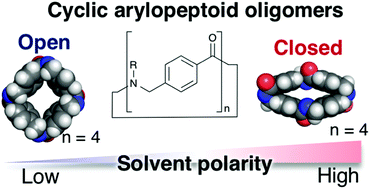
Macrocyclic peptide-mimetic molecules are attracting renewed attention and have found widespread application in research fields ranging from biochemical science to materials science. Herein, we describe the synthesis and structural elucidation of cyclo[n]-p-arylopeptoids (classified into cyclic aromatic ε-amino acids) bearing various side chains, namely, C[n]pAP(Rn) (where n inside brackets denotes the number of main chain units and R inside parentheses represents side chains). We investigate the influence of n and R on the macrocyclization efficiency of linear p-arylopeptoid oligomers (n = 3, 4, 5) under high-dilution conditions with or without slow addition. The structures of the cyclo[4]-p-arylopeptoids (C[4]pAP(Rn)) and their conformational dynamics are disclosed on the basis of single-crystal X-ray analyses, viable-temperature (VT) 1H NMR studies, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. We found two representative conformations (open and closed) of cyclo[4]-p-arylopeptoids (C[4]pAP(Rn)) in the solid state and whose preference in the solution state was most likely dependent on solvent polarity. We believe that this simple but dynamic macrocyclic peptide-mimetic molecular scaffold would be attractive for developing new functional molecular tools based on rational molecular design as well as molecular library screening strategies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...