Stability and anti-inflammatory activity of the reduction-resistant curcumin analog, 2,6-dimethyl-curcumin†
Abstract
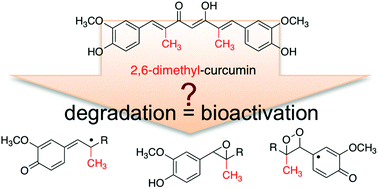
The efficacy of the curry spice compound curcumin as a natural anti-inflammatory agent is limited by its rapid reductive metabolism in vivo. A recent report described a novel synthetic derivative, 2,6-dimethyl-curcumin, with increased stability against reduction in vitro and in vivo. It is also known that curcumin is unstable at physiological pH in vitro and undergoes rapid autoxidative transformation. Since the oxidation products may contribute to the biological effects of curcumin, we tested oxidative stability of 2,6-dimethyl-curcumin in buffer (pH 7.5). The rate of degradation was similar to curcumin. The degradation products were identified as a one-carbon chain-shortened alcohol, vanillin, and two isomeric epoxides that underwent cleavage to vanillin and a corresponding hydroxylated cleavage product. 2,6-Dimethyl-curcumin was more potent than curcumin in inhibiting NF-κB activity but less potent in inhibiting expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. 2,6-Dimethyl-curcumin and some of its degradation products covalently bound to a peptide that contains the redox-sensitive cysteine of IKKβ kinase, the activating kinase upstream of NF-κB, providing a mechanism for the anti-inflammatory activity. In RAW264.7 cells vanillin, the chain-shortened alcohol, and reduced 2,6-dimethyl-curcumin were detected as major metabolites. These studies provide new insight into the oxidative transformation mechanism of curcumin and related compounds. The products resulting from oxidative transformation contribute to the anti-inflammatory activity of 2,6-dimethyl-curcumin in addition to its enhanced resistance against enzymatic reduction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...