Remote functionalization in surface-assisted dehalogenation by conformational mechanics: organometallic self-assembly of 3,3′,5,5′-tetrabromo-2,2′,4,4′,6,6′-hexafluorobiphenyl on Ag(111)†
Abstract
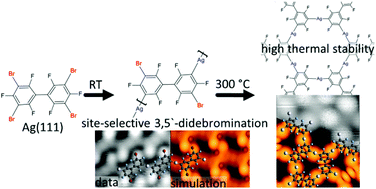
Even though the surface-assisted dehalogenative coupling constitutes the most abundant protocol in on-surface synthesis, its full potential will only become visible if selectivity issues with polybrominated precursors are comprehensively understood, opening new venues for both organometallic self-assembly and on-surface polymerization. Using the 3,3′,5,5′-tetrabromo-2,2′,4,4′,6,6′-hexafluorobiphenyl (Br4F6BP) at Ag(111), we demonstrate a remote site-selective functionalization at room temperature and a marked temperature difference in double- vs. quadruple activation, both phenomena caused by conformational mechanical effects of the precursor-surface ensemble. The submolecularly resolved structural characterization was achieved by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, the chemical state was quantitatively assessed by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, and the analysis of the experimental signatures was supported through first-principles Density-Functional Theory calculations. The non-planarity of the various structures at the surface was specifically probed by additional Near Edge X-ray Absorption Fine Structure experiments. Upon progressive heating, Br4F6BP on Ag(111) shows the following unprecedented phenomena: (1) formation of regular organometallic 1D chains via remote site-selective 3,5′-didebromination; (2) a marked temperature difference in double- vs. quadruple activation; (3) an organometallic self-assembly based on reversibility of C–Ag–C linkages with a thus far unknown polymorphism affording both hexagonal and rectangular 2D networks; (4) extraordinary thermal stability of the organometallic networks. Controlled covalent coupling at the previously Br-functionalized sites was not achieved for the Br4F6BP precursor, in contrast to the comparatively studied non-fluorinated analogue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...