A stable layered P3/P2 and spinel intergrowth nanocomposite as a long-life and high-rate cathode for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
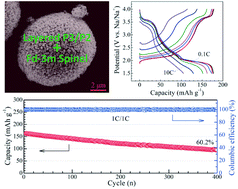
Layered sodium transition-metal oxides, NaxMeO2, with large theoretical capacity are regarded as an important class of cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). However, they usually exhibit inferior thermodynamic stability and sluggish Na+ kinetics due to the unwanted phase transitions and large Na+-ionic radius. In this work, considering the beneficial synergistic effects of layered P2/P3 and Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m spinel phases, a stable layered/spinel intergrowth nanocomposite Na0.5[Ni0.2Co0.15Mn0.65]O2 is rationally designed and successfully prepared via a co-precipitation route and a subsequent solid-state reaction, and the triphase synergy in this layered/spinel nanocomposite is demonstrated. In Na/Na0.5[Ni0.2Co0.15Mn0.65]O2 half-cells, it delivers a high specific capacity of ∼180 mA h g−1 and a good cycling stability, with a capacity retention of 87.6% after 100 cycles, at a rate of 0.1C between 1.5 and 4.0 V (vs. Na/Na+). The large reversible capacity of 105 mA h g−1 is also achieved even at a high rate of 10C, indicating high-rate capability. Besides, the full-cells using this nanocomposite as the cathode and hard carbon as the anode exhibit long-term cycle-life and high-power properties, indicating the expected merits of layered/spinel mixed phases. The superior sodium storage performance of this layered P3/P2 and spinel intergrowth nanocomposite makes it a promising candidate as a long-life and high-rate cathode for SIBs.
m spinel phases, a stable layered/spinel intergrowth nanocomposite Na0.5[Ni0.2Co0.15Mn0.65]O2 is rationally designed and successfully prepared via a co-precipitation route and a subsequent solid-state reaction, and the triphase synergy in this layered/spinel nanocomposite is demonstrated. In Na/Na0.5[Ni0.2Co0.15Mn0.65]O2 half-cells, it delivers a high specific capacity of ∼180 mA h g−1 and a good cycling stability, with a capacity retention of 87.6% after 100 cycles, at a rate of 0.1C between 1.5 and 4.0 V (vs. Na/Na+). The large reversible capacity of 105 mA h g−1 is also achieved even at a high rate of 10C, indicating high-rate capability. Besides, the full-cells using this nanocomposite as the cathode and hard carbon as the anode exhibit long-term cycle-life and high-power properties, indicating the expected merits of layered/spinel mixed phases. The superior sodium storage performance of this layered P3/P2 and spinel intergrowth nanocomposite makes it a promising candidate as a long-life and high-rate cathode for SIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...