Facet-dependent photocatalytic decomposition of N2O on the anatase TiO2: a DFT study†
Abstract
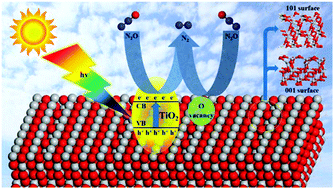
The photocatalytic N2O dissociation on anatase TiO2 is an attractive reaction and the mechanism of the photocalytic process, the role of excited electrons, and the favorable facet for higher activity need a more detailed study at the molecular level. Using DFT + U calculations, we investigate the dissociation process of N2O into N2 with and without photoexcited electrons on anatase TiO2 (001) and (101) facets to unravel such puzzles. The optical absorption properties of TiO2 (001) and (101) facets are compared in combination with electronic analysis. The localization of excited electrons on the two surfaces with the existence of oxygen vacancies is explored. When there is no photo-excitation, on a perfect TiO2 surface, N2O decomposition is difficult due to the inhibitive high reaction energy. In contrast, the reaction energy decreases dramatically in the presence of photoexcited or excess electrons on the TiO2 surface. The reaction energy is related to the electronic state of dissociated O. The more negative charges make O more stable, and accordingly lead to higher exothermic reaction energy. Based on this point, the influence of surface morphology and excited states can be understood. This is the first theoretical study of the photocatalytic process of N2O elimination, which will guide further experimental study and improve its activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...