Engineering TiO2 supported Pt sub-nanoclusters via introducing variable valence Co ion in high-temperature flame for CO oxidation
Abstract
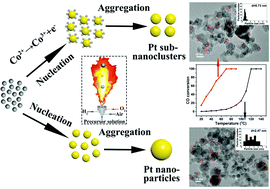
As a typical catalytic reaction model, CO catalytic oxidation has many practical applications in gas purification. TiO2 supported Pt sub-nanoclusters have been prepared by introducing variable valence Co ions into a one step flame spray pyrolysis process. Co2+ was oxidized to Co3+ in the high-temperature flame, and the released electrons were transferred to the surface of Pt and suppressed the aggregation of Pt nanoclusters supported on TiO2. As a result, the average size of Pt nanoclusters reduced from 2.47 nm to 0.72 nm with only 1% Co2+ ion doping. Moreover, due to the presence of Co, surface oxygen species were also affected, and these changes also led to a significant increase in the catalytic activity of CO oxidation. The temperature at 100% conversion was decreased from 120 °C to 70 °C, and the TOF increased by an order of magnitude. In addition, in situ DRIFTS was also used to investigate the cause of the significant increase in activity, and it was shown that adsorbed CO species on Pt could be desorbed more easily because of the electron transfer between Pt and Co species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...