Ce-Doped bundled ultrafine diameter tungsten oxide nanowires with enhanced electrochromic performance†
Abstract
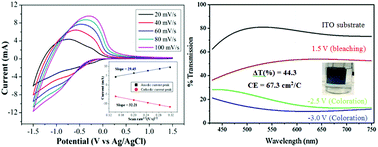
Cerium (Ce)-doped tungsten oxide nanostructures were synthesised using a simple solvothermal method from cerium chloride salt (CeCl3·7H2O) and tungsten hexachloride (WCl6) precursors. The as-prepared samples were thoroughly characterised using electron microscopies, X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy. The electrochromic performance of different samples was evaluated using a custom-built UV-VIS spectrometer and an electrochemistry technique. The results showed that the as-prepared samples underwent morphological evolution with the increase in the Ce/W molar ratio, from long, thin and bundled nanowires, through shorter and thicker nanowires to mixed nanowire bundles and nanoparticle agglomerates. From electrochemical testing, we found that the Ce-doped tungsten oxides exhibited higher optical contrasts of 44.3%, 49.7% and 39.4% for the 1 : 15, 1 : 10 and 1 : 5 Ce/W ratios respectively, compared with 37.4% for the pure W18O49 nanowires. The Ce/W = 1 : 15 samples presented an improved colouration efficiency of 67.3 cm2 C−1 against 62 cm2 C−1 for pure W18O49. This work demonstrated that the Ce-doped W18O49 nanowires are very promising candidate materials for the design and construction of electrochemical chromic devices with largely improved efficiency, contrast and stability. The results from this work suggested that smart electrochromic devices based on current Ce-doped WOx nanomaterials could be further developed for future energy-related applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...