Li0.93V2.07BO5: a new nano-rod cathode material for lithium ion batteries
Abstract
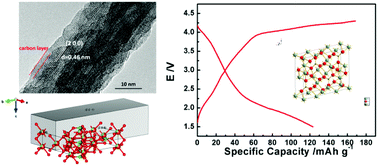
The compound Li0.93V2.07BO5 (LVBO) has been successfully designed and used for the first time as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries (LIBs). It belongs to a new family of lithium transition metal borates, namely LiMBO3 (M = Mn, Fe or Co), which are regarded as good alternatives to phosphates because of their comparably lower molecular weights, which can lead to a larger theoretical specific capacity than those of phosphate-based LiMPO4. LVBO crystallizes in the space group Pbam with V atom and Li atom occupying the same sites, which makes the structure more stable and brings a disorder effect. Further structure and components of the promising cathode material have been characterized based on the results of X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The synthesized LVBO/C material displays a nanorod morphology with a size of 20–100 nm and shows good electrochemical activity. When used as cathode material in LIBs, LVBO/C delivers an initial discharge specific capacity of 125 mA h g−1 and exhibits relatively good cycle stability. These results are of great interest for further study of its electrochemical behaviors, which is of significance in exploring new borate cathode materials for LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...