Monitoring the dynamics of cell-derived extracellular vesicles at the nanoscale by liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy†
Abstract
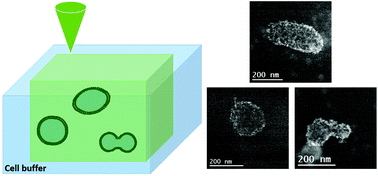
Cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) circulating in body fluids hold promises as bioactive therapeutic agents and as biomarkers to diagnose a wide range of diseases. However nano-imaging methods are needed to characterize these complex and heterogeneous soft materials in their native wet environment. Herein, we exploit liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy (LCTEM) to characterize the morphology and dynamic behavior of EVs in physiological media with nanometer resolution. The beam-induced controlled growth of Au nanoparticles on bilayer membranes is used as an original in situ staining method to improve the contrast of EVs and artificial liposomes. LCTEM provides information about the size distribution and concentration of EVs that are consistent with Cryo-TEM and nanoparticle tracking analysis measurements. Moreover, LCTEM gives a unique insight into the dynamics of EVs depending on their liquid environment. The size-dependent morphology of EVs is sensitive to osmotic stress which tends to transform their spherical shape to ellipsoidal, stomatocyte or discocyte morphologies. In the liquid-cell, EVs exhibit a sub-diffusive motion due to strong interactions between the Au nanoparticles and the liquid-cell windows. Finally, the high-resolution monitoring of EV aggregation and fusion illustrate that LCTEM opens up a new way to study cell-membrane dynamics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...