Glucose oxidase-loaded liposomes for in situ amplified signal of electrochemical immunoassay on a handheld pH meter
Abstract
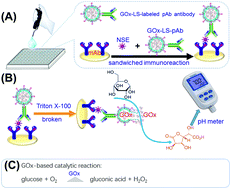
Methods based on a pH meter have been developed for immunoassays, but most involve low sensitivity and weakly detectable signals, and thus are unsuitable for routine use. Herein, a simple and portable electrochemical immunoassay was designed for sensitive screening of a disease-related biomarker, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), by using glucose oxidase-loaded liposomes (GOx-LS) for signal amplification. Initially, a sandwiched immunoreaction was performed on rabbit anti-human monoclonal NSE antibody-coated microplate with polyclonal rabbit anti-human NSE antibody-labeled GOx-LS. Thereafter, the GOx-LS accompanying the immunocomplex could oxidize glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide, thus resulting in the pH change of the detection solution, which could be registered on a handheld pH meter. Relative to GOx-labeling, use of GOx-LS could amplify the signal of the electrochemical immunosensing platform. Under optimum conditions, the GOx-LS-based immunoassay exhibited good pH responses toward target NSE within the dynamic linear range of 0.01–100 ng mL−1 with a detection limit of 8.9 pg mL−1. The coefficients of variation for the reproducibility and precision of this method were less than 7.9% and 12.7% for the single-batch and different-batch identification, respectively. High specificity and acceptable stability were acquired for determining target NSE using this method. For the detection of human serum specimens, well-matched results were provided between pH-based immunoassay and commercial Electrochemiluminescent Automatic Analyzer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...