Detection and discrimination of Zn2+ and Hg2+ using a single molecular fluorescent probe†
Abstract
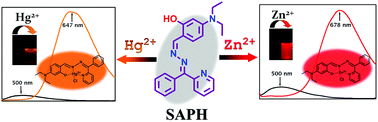
A new fluorescent probe (SAPH) has been introduced which shows specific sensing towards Zn2+ and Hg2+ at two different wavelength maxima at physiological pH. The probe shows a brilliant ratiometric red shift in emission spectra upon addition of Zn2+ at 678 nm while upon addition of Hg2+ it shows a turn-on ratiometric emission enhancement with a red shift at 647 nm. Job's plot confirms the 1 : 1 complexation for both Zn2+ and Hg2+. The binding constants have been calculated using the Benesi–Hildebrand equation and found to be 3.03 × 105 M−1 and 6.05 × 104 M−1 respectively for SAPH–Zn2+ and SAPH–Hg2+. DFT and TDDFT studies are conducted using the probe to establish a similarity between theoretical and experimental outcomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...