Predicting the skin-permeating components of externally-applied medicinal herbs: application of a newly constructed linear free-energy relationship equation for human skin permeation†
Abstract
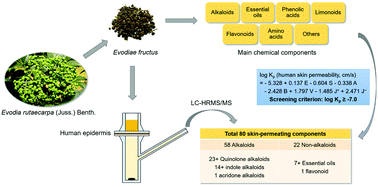
A linear free-energy relationship (LFER) equation that is able to provide a valid prediction of the skin permeability coefficients (log Kp) of neutral molecules, ions and ionic species has recently been constructed and optimized. This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of predicting the skin-permeating components (SPCs) of externally applied herbs using the LFER equation, with Evodiae fructus (EF) taken as a model herb. The log Kp values of the reported chemical components of EF at pH 4.0 were calculated using the LFER equation and their structural descriptors. The results showed that the essential oils, quinolone, acridone and indole alkaloids of EF are more permeable when compared to other main components, such as phenylpropanoids, furoquinoline alkaloids, limonoids and flavonoids. The SPCs of EF were further collected via ex vivo skin permeation experiments, and analyzed by liquid chromatography-high resolution tandem mass spectrometry. A total of 80 SPCs were detected, and part of them were tentatively identified based on their empirical molecular formulae and MS/MS spectra. The SPCs are made up of 58 alkaloids, including 23 or more quinolone alkaloids, 14 or more indole alkaloids and 1 acridone alkaloid, and 22 non-alkaloids, including 7 or more essential oils and 1 flavonoid, which is in good agreement with the prediction by the LFER equation. It is suggested that a log Kp of −7.0 may be considered as a borderline, above which are potential SPCs and below which are non-SPCs. Very interestingly, the primary SPCs give a good explanation to the antihypertensive action of externally applied EF. To sum up, the LFER equation can be used to predict the SPCs of externally applied herbs, and thus to narrow the range of their potential effective components and speed up the pharmacological study.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...