Study of interactions of mononucleotides with 1,4-dihydropyridine vesicles using NMR and ITC techniques†
Abstract
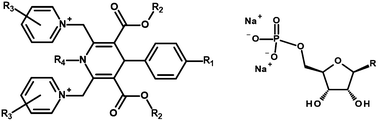
The use of 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP) vesicles as drug delivery agents can improve the diffusion of nucleoside and nucleotide prodrugs through the cellular membrane without degradation. Different NMR studies: spin–lattice relaxation in the rotating frame (T1ρ), saturation transfer double difference (STDD), 1H NMR chemical shift titration, as well as isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) experiments, showed that mononucleotides bind to 1,4-DHP vesicles. The influence of the structure of the mononucleotides as well as that of the derivatives of 1,4-DHP on the complexation parameters was studied.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...