Bipyridine bisphosphonate-based fluorescent optical sensor and optode for selective detection of Zn2+ ions and its applications†
Abstract
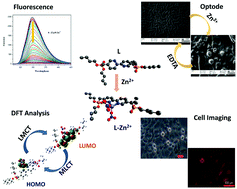
In this study, a bipyridine bisphosphonate-based tetrabutyl 2,2′-bisbipyridine-5,5′-diylbis(methylene) diphosphonate (L) was developed as fluorescence optical sensor for sensitive and selective determination of Zn2+. The sensing ability of L was investigated in solution as well as polymeric membrane phase using absorption and emission spectroscopy. L exhibits weak fluorescence in CH3CN/H2O (9 : 1, v/v). Upon interaction of L with Zn2+ ions, the emission intensity of L significantly increases due to chelation-enhanced fluorescence (CHEF). The Job's plot and Benesi–Hildebrand (B–H) studies revealed the formation of a L–Zn2+ complex in 1 : 1 binding stoichiometry with an estimated association constant of 4.2 × 103 M−1. The complex formation between L and Zn2+ was established from 1H NMR, 31P NMR, mass and theoretical studies. In order to make a low-cost and effective probe for sensing Zn2+ in aqueous media, the optode was prepared by incorporating L as a neutral ligand, dioctyl phthalate (DOP) as plasticizer, sodium tetraphenyl borate (NaTPhB) as an anionic additive and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) as supporting membrane. These components were systematically coated on a quartz plate of dimensions 12 mm × 16 mm with 5 mm thickness. After equilibration with Zn2+, the optode exhibited a selective and strong fluorescence at 350 nm due to CHEF. The best performance of the optode was observed with a membrane having L : PVC : DOP : NaTPhB in proportions of 2 : 62 : 35 : 1 (w/w) in 4.5–8.5 pH range. The probe can detect Zn2+ at concentrations as low as 1.3 nM with fast response time of 15 s and the optical response remains unaltered even after 3 months of use. The fluorescence reversibility of L was studied by sequential addition of Zn2+ and EDTA. The probe was used successfully used for determination of Zn2+ in pharmaceutical and water samples. In addition, L was applied for Zn2+ ions determination in HeLa cells using optical fluoroscence microscope.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...