A dual-cycling biosensor for target DNA detection based on the toehold-mediated strand displacement reaction and exonuclease III assisted amplification†
Abstract
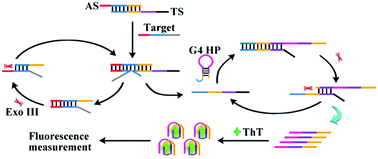
Sensitive detection of disease-related DNA is of great significance for early and accurate diagnosis and therapy. To achieve this aim, we constructed a dual-cycling amplification biosensor for target oligonucleotide detection. Based on the toehold-mediated strand displacement reaction (TSDR), target DNA competitively hybridized with the assistant DNA which previously formed a duplex complex with the trigger DNA, and the trigger DNA was released. Exonuclease III (Exo III) would specially hydrolyze the assistant DNA in the new duplex DNA to free the target DNA for a new cycle. Similarly, based on the TSDR and Exo III assisted amplification, the released trigger DNA would repeatedly open the G-quadruplex hairpins and promote the generation of numerous G-quadruplex sequences. Then, the fluorescence intensity of Thioflavin T (ThT) would present apparent enhancement due to the formation of the G-quadruplex/ThT complex. The commercially available ThT is economical and of low toxicity. More importantly, owing to its satisfactory water solubility, ThT effectively avoids the introduction of organic solvents. There was no need for expensive modification through the whole process. The proposed method displayed high distinction efficiency towards target DNA against mismatched DNA. Additionally, the linear range of this strategy was 0.2–10 nM, and the detection limit was 0.04 nM. Besides, this sensor can be applied in human serum with satisfactory results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...