Folic acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots with tunable fluorescence emission for cancer cell imaging and optical detection of Hg2+†
Abstract
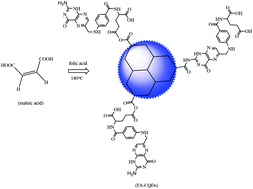
Functional groups may alter the optical and electrical characteristics of graphene quantum dots and lead to unusual properties and related applications. The paper reports a facile synthesis of folic acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots (FA-GQDs) via thermal pyrolysis of maleic acid (MA) and folic acid (FA). The resulting FA-GQDs display a strong and tunable fluorescence emission under visible light excitation. Interestingly, the fluorescence emission depends on the ratio of FA/MA used in the synthesis of FA-GQDs and the excitation wavelength. FA groups were covalently anchored at the edge of graphene sheets, thus FA-GQDs can be used as a turn-on fluorescent probe for folate receptor-positive cancer cells. The uptake of designed FA-GQDs by HepG2 cells was verified by confocal laser scanning microscopy. FA-GQDs also provide a highly sensitive and selective fluorescence response to Hg2+. The peak fluorescence intensity linearly decreases with the increase of Hg2+ in the concentration range of 2.0 × 10−6–5.0 × 10−12 M with a detection limit of 1.7 × 10−12 M (S/N = 3). All metal and nonmetallic ions tested don’t interfere with the optical detection of Hg2+. The analytical method provides better sensitivity and selectivity compared with previously reported optical sensors for Hg2+, which has been successfully applied for the determination of Hg2+ in natural water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...