Ultrahigh yield of hydrogen peroxide and effective diclofenac degradation on a graphite felt cathode loaded with CNTs and carbon black: an electro-generation mechanism and a degradation pathway†
Abstract
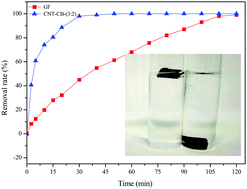
A new graphite felt cathode loaded with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) was developed. The resulting electrode showed a very high generation rate of H2O2 (10.73 mg h−1 cm−2) at a relatively low electric energy consumption (6.90 kW h kg−1). These features improved the in situ production of H2O2 by about 20 folds when an optimized ratio of CNTs to carbon black mass (3 : 2) was used. Several manufacturing parameters like the ratio and loads of CNTs were optimized. Also, factors influencing the electro-generated H2O2, such as pH and current density, were investigated. Examination of H2O2 electro-generation mechanisms indicated that some cathode features would accelerate the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and enhance the electrochemical behavior during H2O2 production. The removal rate of diclofenac by electro-Fenton (EF) using a CNT loaded cathode reached over 99% within 30 min. The total organic carbon (TOC) removal of diclofenac approached 91.71% at 180 min, which was over 4 folds higher than that obtained with the unloaded electrode (19.05%). LC-MS analyses allowed building a possible mechanism and a degradation pathway of diclofenac. In terms of stability, the CNT loaded electrode revealed excellent stability as the removal of TOC was maintained at 87.4% of the original response after ten runs. Such CNT loaded cathodes with efficient and significantly enhanced H2O2 production offer efficient and low energy consumption degradation of organic pollutants by EF.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...