In situ precipitation of hydrous titanium dioxide for dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of nucleosides and their separation
Abstract
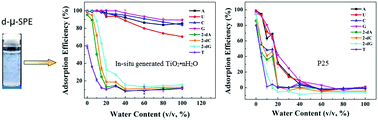
Pure titanium dioxide (TiO2) adsorbent failed to selectively capture ribonucleosides in biological samples, as reported in previous studies, although it was expected to display a specific recognition of cis-diol compounds by the Lewis acid sites on its surface. However, in this work, our results showed for the first time that hydrous titania (TiO2·nH2O), obtained through hydrolysis of tetrabutyl titanate (TBOT) in aqueous solution, exhibited a high affinity for cis-diol-containing ribonucleosides. The adsorption efficiency of A, C and G by TiO2·nH2O can reach about 90% even in a 100% water matrix. On the other hand, the 2′-deoxynucleosides could only be adsorbed in a water–acetonitrile solution with a water content of less than 10%. Subsequently, an in situ-generated TiO2·nH2O-based dispersive micro solid-phase extraction (d-μ-SPE) process was developed and evaluated. The whole d-μ-SPE process takes only about 7 minutes (2 min for extraction and 5 min for centrifugation) and no pre-synthesized or commercial TiO2 powder is required. The hydrous TiO2-based d-μ-SPE with a two-step elution strategy was successfully performed for the extraction and separation of ribonucleosides (A, U) and 2′-deoxynucleosides (2′-dC, 2′-dG) in porcine plasma samples. The proposed TiO2·nH2O-based d-μ-SPE method is effective, simple and rapid, and will have wide application for the selective extraction of cis-diol molecules in environmental and biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...