Stereospecific ligands and their complexes. XXIV. Synthesis, characterization and some biological properties of Pd(ii) and Pt(ii) complexes with R2-S,S-eddtyr†‡
Abstract
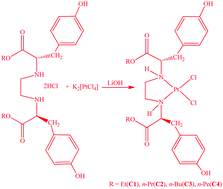
Four new platinum(II) complexes of general formula [PtCl2(R2-S,S-eddtyr)] (R = ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl and n-pentyl); S,S-eddtyr = ethylenediamine-N,N′-di-(2,2′-di(4-hydroxy)-benzyl-acetic acid) have been synthesized and characterized by microanalysis, and infrared, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The in vitro antimicrobial activity of ligands L1–L4 [L = R2-S,S-eddtyr; R = ethyl (L1), n-propyl (L2), n-butyl (L3), n-pentyl (L4)], platinum(II) complexes C1–C4 [PtCl2(R2-S,S-eddtyr)] [R = ethyl (C1), n-propyl (C2), n-butyl (C3), n-pentyl (C4)] and palladium(II) complexes C5–C8 [PdCl2(R2-S,S-eddtyr)] [R = ethyl (C5), n-propyl (C6) or n-butyl (C7) or n-pentyl (C8)] was investigated. The cytotoxicity of ligands and platinum(II) complexes was investigated using MTT assay. The interaction of platinum and palladium complexes [MCl2(R2-S,S-eddtyr)] (M = Pt or Pd) with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) was investigated using UV-Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. The association constant (Kb) estimated from the absorption spectral study and the quenching constant (KSV) calculated from relevant fluorescence quenching data indicate a non-covalent interaction between the metal complex and DNA. Ethidium bromide (EB) competitive studies revealed that complexes C1–C8 could interact with CT-DNA through intercalation. Furthermore, the interactions between human serum albumin (HSA) and the platinum(II) and palladium(II) complexes were also investigated by UV-Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy, showing that the new complexes could strongly bind with HSA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...