BSA capped bi-functional fluorescent Cu nanoclusters as pH sensor and selective detection of dopamine
Abstract
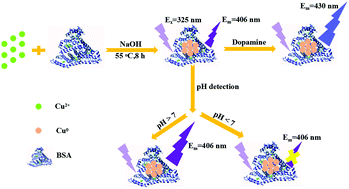
In this study, a facile and environment-friendly method for the preparation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) capped fluorescent Cu nanoclusters (BSA-CuNCs) was adopted. The as-prepared BSA-CuNCs were characterized by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), fluorescent spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The fluorescence excitation and emission wavelength of BSA-CuNCs appeared at 325 and 406 nm, respectively. The as-synthesized BSA-CuNCs can be utilized as a bi-functional nanomaterial for pH sensing and dopamine (DA) detection with good performance. The fluorescence intensity decreased linearly with decrease in pH from 12 to 5 and increased linearly with increase in DA concentration from 0.5 to 50 μM. TEM measurements proved that the decrease in the pH value resulted in the aggregation of BSA-CuNCs, leading to color change and the quenching of fluorescence. The FT-IR spectra, fluorescent spectra, UV-Vis spectra and zeta potential measurements demonstrated that DA can be combined with Cu2+ and the Cu2+ would be removed from the surface of BSA-CuNCs. As a result, the fluorescence was recovered owing to the formation of the highly stable compound CuH2(DA)2. The pH value of five water samples was determined by the proposed method with relative errors of less than 0.91%. Furthermore, DA in human urine samples was also analyzed by BSA-CuNCs with good recoveries ranging from 90.4% to 104.7% using the standard addition method. It is believed that the bi-functional BSA-CuNCs will show great potential in bio-systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...