Trehalose elevates brain zinc levels following controlled cortical impact in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury
Abstract
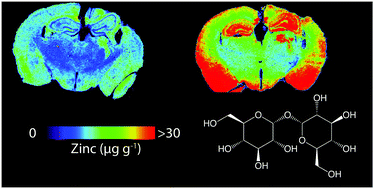
Zinc (Zn) deficiency is a clinical consequence of brain injury that can result in neuropathological outcomes that are exacerbated with age. Here, we present laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) imaging data showing modulation of brain Zn levels by the disaccharide trehalose in aged mice following a controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury. In this proof-of-concept study, trehalose induced an increase in brain zinc levels, providing important preliminary data for larger studies using this simple carbohydrate as a modulator of this essential micronutrient in traumatic brain injury. Our results may have further implications for the treatment of a variety of neurodegenerative diseases and other disorders of the nervous system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...