The semi-synthesis, biological evaluation and docking analysis of the oxime, hydrazine and hydrazide derivatives of platensimycin†
Abstract
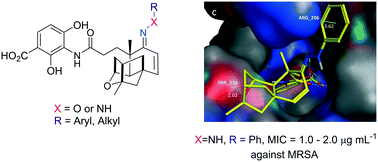
A dozen oxime, hydrazine and hydrazide derivatives of platensimycin (PTM) analogues were synthesized, some of which showed strong antibacterial activities and were shown to be stable under the bioassay conditions. Docking analysis revealed that they have certain new interactions with β-ketoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] synthase II (FabF), suggesting that Schiff base formation on its terpene scaffold is an effective strategy to diversify PTM structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...