Ga-doped Cu/H-nanozeolite-Y catalyst for selective hydrogenation and hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived chemicals†
Abstract
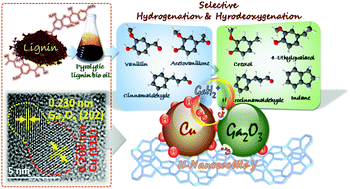
The development of an efficient non-sulfided and non-precious catalyst for selective hydrogenation (HD) and hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of biomass-derived feedstocks to produce fuels and chemicals is of great interest. In this study, a highly efficient bimetallic Ga-doped Cu/H-nanozeolite-Y (Cu/HNZY) catalyst was developed for selective HD and HDO of lignin-derived species (vanillin, acetovanillone, and cinnamaldehyde) under mild conditions (120–180 °C, 1 MPa H2). The HNZY support exhibited a mesoporous structure with a large external surface area, which can facilitate reactant adsorption. Ga doping not only increased the Cu dispersion and Lewis acidity, but produced low coordinated Ga species (e.g., Ga+ and (GaH2)+), which could enhance the HDO activity. As a result, at 160 °C for 2 to 5 h, complete conversion of vanillin and acetovanillone into their decarbonylated species (creosol and 4-ethylguiuacol) with high selectivity (>99%) could be achieved at a low H2 initial pressure of 1 MPa. In addition, when cinnamaldehyde was converted over Ga-doped Cu/HNZY at 180 °C, selective HD and HDO followed by cyclization formed high amounts of indane and its derivatives, which have a variety of applications in pharmaceutical and agricultural industries. This could open a new possibility for lignin-to-drug intermediates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...