Facile synthesis of starch-based nanoparticle stabilized Pickering emulsion: its pH-responsive behavior and application for recyclable catalysis†
Abstract
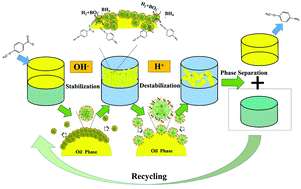
In this work, a pH-responsive [2-(dimethylamine)ethyl methacrylate] (DMAEMA) grafted maize starch composite was synthesized via free radical polymerization in the presence of the crosslinker N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS). Combined with the gelatinization–ethanol precipitation process, this starch-based composite in an optimized component ratio showed a nanometer size and regular spherical shape, along with a high freedom of the molecular chain, which was not only a breakthrough in terms of structure, but also brought about an outstanding performance in pH-responsiveness. Its superiority was proved by the formation of a Pickering emulsion that underwent pH-induced reversible emulsification/demulsification for at least 8 cycles without obvious performance decay or even morphology changes. Dynamic light scattering, zeta potential measurement and interfacial tension measurement, as well as contact angle measurement, confirmed synergistically that the reversible emulsification/demulsification cycle was the result of the tunable wettability and size of these novel starch-based nanoparticles under pH variation. More importantly, benefitting from DMAEMA as the stabilizer and growth point for Au nanoparticles and the large interfacial area of the emulsion droplets together with the pH-responsive reversible emulsification/demulsification cycle, the generated Pickering emulsion could be readily applied as catalytic microreactors for the hydrogenation of p-nitroanisole at the oil–water interface. This catalysis exhibited both high catalytic activity and good recyclability. The excellent performance makes us believe that this system is promising for meeting the requirements of green and sustainable chemistry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...