Thermal and photocatalytic oxidation of organic substrates by dioxygen with water as an electron source
Abstract
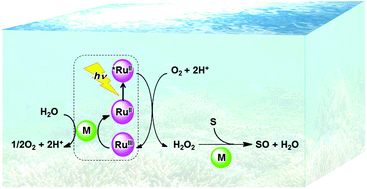
The oxidation of organic substrates is of fundamental importance in nature and includes key transformations in organic synthesis and industry. Dioxygen (O2) is potentially the greenest oxidant because O2 is available in air and its reduction product is water, which is environmentally the most benign substance. However, the direct thermal oxidation of organic substrates with O2 is spin-forbidden because the spin state of ground-state O2 is triplet and the spin state of most organic substrates is singlet. Transition metal complexes can react with triplet O2 in the presence of an electron source to produce metal–oxygen intermediates, such as metal-oxo and metal-hydroperoxo complexes, that can oxidize substrates under mild conditions. Various thermal and photocatalytic mechanisms of the oxidation of organic substrates by O2 with transition metal complexes have been critically discussed by focusing on how metal–oxygen intermediates are produced in the presence of an electron source and then react with organic substrates. Metal–oxygen intermediates are more easily produced by the reactions of metal complexes with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and act as active catalysts for the oxidation of substrates by H2O2. The photocatalytic oxidation of water by O2 to produce H2O2 has been combined with the catalytic oxidation of organic substrates by H2O2 to achieve the photocatalytic oxidation of organic substrates by O2. The photocatalytic oxidation of organic substrates by O2 with the use of water as an electron source has also been made possible by the use of inorganic and organic photocatalysts, which can be combined with transition metal complexes as catalysts for thermal reaction steps.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...