Ruthenium(ii) oxidase catalysis for C–H alkenylations in biomass-derived γ-valerolactone†
Abstract
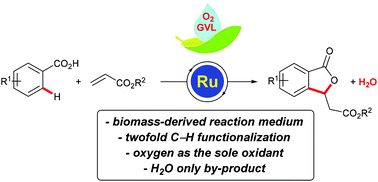
Ruthenium(II) biscarboxylate oxidase catalysis is a powerful tool for the assembly of functionalized arenes with oxygen as a green oxidant, but this strategy was thus far limited to its use in traditional organic solvents. Herein, we report on a green procedure for the ruthenium(II) biscarboxylate-catalysed C–H functionalisation in biomass-derived γ-valerolactone as the reaction medium. The oxidase catalysis was characterized by ample substrate scope and proceeded efficiently with oxygen as the sole oxidant. The overall green nature of this C–H-activation methodology is reflected by H2O being the only by-product.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...