A comparative study of EPA-enriched ethanolamine plasmalogen and EPA-enriched phosphatidylethanolamine on Aβ42 induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
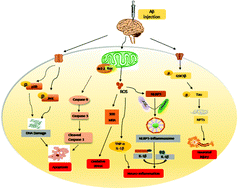
Ethanolamine plasmalogen (pPE), a major phospholipid in neuronal membranes, is specifically reduced in postmortem brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The purpose of the present study was to compare the effects of EPA-enriched ethanolamine plasmalogen (EPA-pPE) and EPA-enriched phosphatidylethanolamine (EPA-PE) on cognitive deficiency and illustrate the possible underlying mechanisms. SD rats were divided into four groups including the sham group injected with 0.9% saline and three amyloid-β (Aβ) infusion groups, Aβ42 group, EPA-pPE group and EPA-PE group. EPA-pPE and EPA-PE were administered by gavage (150 mg kg−1 day−1), respectively, once a day for 26 days. Administration of EPA-pPE exerted better effects than EPA-PE in improving Aβ-induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Further mechanical research indicated that EPA-pPE was superior to EPA-PE in regulating oxidative stress via increasing SOD activity and decreasing MDA level, as well as reducing GSK-3β and tau phosphorylation. Moreover, EPA-PE was more effective than EPA-pPE at inhibiting the protein expressions of Bax and caspase 9. The results of neuro-inflammation and inflammasome activation showed that EPA-pPE exerted more significant effects than EPA-PE in inhibiting the expressions of TNF-α and IL-1β, and decreasing NLRP3, pro-caspase 1 and caspase 1 levels. EPA-pPE alleviated Aβ-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress, neuronal injury, apoptosis and neuro-inflammation, which might depend on the vinyl ether linkage at the sn-1 position.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...