The protective role of Ocimum basilicum L. (Basil) against aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice: Impact on oxidative stress, inflammation, motor deficits and anxiety-like behavior
Abstract
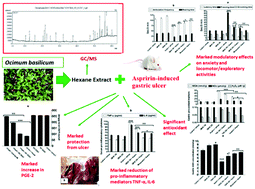
The gastroprotective effect of Ocimum basilicum L. (Basil) hexane extract (OBHE) in aspirin-induced gastric ulcers in mice and its ameliorative effect on behavioral alterations were determined. Pretreatment with OBHE (100 or 200 mg kg−1) or misoprostol (50 μg kg−1) alleviated the aspirin-induced oxidative stress by significantly decreasing (p < 0.001) gastric ulcer index scores (57, 76 and 79%), gastric TBARS (by 49, 51 and 52%), NO (21, 28 and 29%), H2O2 (24, 42 and 45%), and the serum pro-inflammatory mediator TNF-α (21, 53 and 53%) and IL-6 (29, 30 and 31%), as well as by markedly increasing gastric GSH (41, 61 and 70%), GSH-Px (21, 32 and 34%), GST (33, 63 and 70%), GR (90, 99 and 112%), CAT (167, 211 and 267%) and serum PGE-2 levels (22, 135 and 200%) and IL-4 (64, 81 and 104%), respectively, compared with the aspirin-treated group. Meanwhile, OBHE and misoprostol induced a significant decrease (p < 0.001) in the freezing time (53, 56 and 64%), and the grooming time (by 25, 43 and 44%), respectively, compared to the aspirin treated group. This study provides evidence that OBHE confers anxiolytic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory prophylactic effects on aspirin-induced gastric ulcers. GC/MS was used for the characterization of OBHE components. Based on the findings of this study, basil may be used as a nutritional supplement or therapeutic drug to protect against aspirin-induced gastric ulcers, a common problem resulting from the use of aspirin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...