Milk fat protects Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bb-12 from in vitro gastrointestinal stress in potentially synbiotic table spreads
Abstract
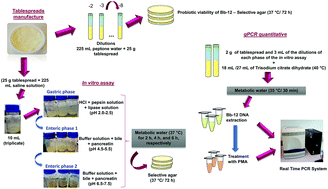
The viability and the in vitro gastrointestinal survival of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bb-12 (Bifidobacterium Bb-12) in table spreads with different proportions of milk fat (MF) and palm olein (PO) (MF : PO 40 : 60 and MF : PO 20 : 80) were investigated for up to 28 days of storage at 5 °C. Moreover, qPCR alone and combined with propidium monoazide (PMA) were compared with the traditional plate count method for determining the in vitro gastrointestinal survival of Bifidobacterium Bb-12 in table spreads after 35 days of storage. Formulations showed probiotic viabilities ranging from 8 to 9 log CFU g−1 across the whole storage period, and the milk fat and palm olein in different concentrations did not affect this viability. Bifidobacterium Bb-12 showed good survival after six hours under in vitro simulated gastrointestinal conditions during the studied storage period, with average reductions of 1.70 (MF : PO 40 : 60) and 2.16 log CFU g−1 (MF : PO 20 : 80). The results of the qPCR with PMA treatment and the plate count method were similar and the qPCR without PMA treatment was shown to overestimate the Bifidobacterium Bb-12 populations. However, the MF : PO 40 : 60 spread showed a Bb-12 population between 0.76 and 1.43 log CFU g−1 higher than that of MF : PO 20 : 80. Thus, the results showed that table spreads, especially food matrices with a higher proportion of milk fat, are suitable for the incorporation of Bifidobacterium Bb-12.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...