Ginnalin A from Kujin tea (Acer tataricum subsp. ginnala) exhibits a colorectal cancer chemoprevention effect via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway†
Abstract
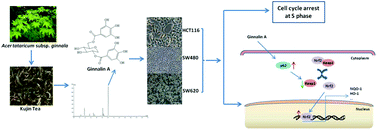
Ginnalin A (also known as acertannin) is one of the most important phenolic compounds of several beverage Acer plants. In this study, it is reported for the first time that ginnalin A is an activator of the Nrf2 signaling pathway in human colon cancer cells. Ginnalin A, isolated from the leaves of Acer tataricum subsp. ginnala, exhibited promising preventive activity against colon cancer cells (HCT116, SW480 and SW620) with IC50 values of 24.8 μM, 22.0 μM and 39.7 μM, respectively. In addition, it significantly reduced the colony formation of these cells. Flow cytometry analysis indicated that ginnalin A suppressed cancer proliferation via the induction of cell cycle arrest at the S-phase. Real time PCR analysis demonstrated that ginnalin A can upregulate the mRNA expression levels of Nrf2-related antioxidant genes Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1. Western blotting analysis revealed that ginnalin A promoted the Nrf2 nuclear translocation and upregulated the proteins Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1. Moreover, the upregulation of p62 and the inhibition of Keap1 were also found by Western blotting analysis. Therefore, the activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway was probably induced through the upregulation of p62 and the inhibition of Keap1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...