Isoenergic modification of whey protein structure by denaturation and crosslinking using transglutaminase†
Abstract
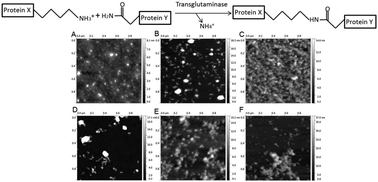
Transglutaminase (TG) catalyzes formation of covalent bonds between lysine and glutamine side chains and has applications in manipulation of food structure. Physical properties of a whey protein mixture (SPC) denatured either at elevated pH or by heat-treatment and followed by TG catalyzed crosslinking, have been characterised using dynamic light scattering, size exclusion chromatography, flourescence spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. The degree of enzymatic crosslinking appeared higher for pH- than for heat-denatured SPC. The hydrophobic surface properties depended on the treatment, thus heating caused the largest exposure of the hydrophobic core of SPC proteins, which was decreased by crosslinking. The particle size of the treated SPC samples increased upon crosslinking by TG. Moreover, the particle morphology depended on the type of denaturing treatment, thus heat-treated SPC contained fibrillar structures, while pH-denatured SPC remained globular as documented by using atomic force microscopy. Finally, the in vitro digestability of the different SPC samples was assessed under simulated gastric and intestinal conditions. Notably heat-treatment was found to lower the gastric digestion rate and enzymatic crosslinking reduced both the gastric and the intestinal rate of digestion. These characteristics of the various SPC samples provide a useful basis for design of isoenergic model foods applicable in animal and human studies on how food structure affects satiety.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...