Ultraviolet irradiation sensitizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to multiple antibiotics†
Abstract
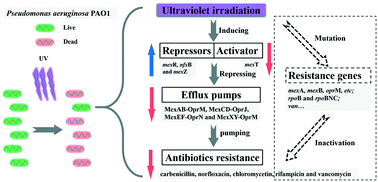
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation has been widely used as an effective disinfection technology in water or wastewater treatment, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an opportunistic pathogen with multiple-antibiotic resistance (AR), prevails in aquatic environments. However, UV effects on the AR profiles of the surviving P. aeruginosa still remain unknown. This study investigated the changing patterns of antibiotic susceptibility of the surviving P. aeruginosa after UV disinfection. Antibiotic susceptibility tests indicated that the surviving P. aeruginosa seemed more susceptible to norfloxacin, carbenicillin, rifampicin, vancomycin and chloromycetin after UV irradiation (P-value <0.05), and the AR pattern changes showed fine hereditary stability. Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR indicated that UV irradiation upregulated mRNA expression of mexR for nearly all time durations, nfxB for a short time and mexZ for a long time (P-value <0.05) and downregulated mRNA expression of mexT for a long time (P-value <0.05), and subsequently inhibited the activities of the efflux pumps, due to mexR, nfxB and mexZ as repressors negatively regulating MexAB-OprM, MexCD-OprJ and MexXY-OprM, respectively, and mexT as an activator positively regulating both MexAB-OprM and MexEF-OprN. The disturbance of the regulatory system of efflux pumps by UV irradiation increased the multiple-antibiotic susceptibility of surviving P. aeruginosa PAO1. The results may extend our knowledge regarding the UV effects on bacterial AR and practically help regulate and optimize water or wastewater disinfection processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...